Doubly Linked List
"""
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list
"""
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.previous = None
self.next = None
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.data}"
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def __iter__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_head('b')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_head('a')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('c')
>>> tuple(linked_list)
('a', 'b', 'c')
"""
node = self.head
while node:
yield node.data
node = node.next
def __str__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('a')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('b')
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail('c')
>>> str(linked_list)
'a->b->c'
"""
return "->".join([str(item) for item in self])
def __len__(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> for i in range(0, 5):
... linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
>>> len(linked_list) == 5
True
"""
return sum(1 for _ in self)
def insert_at_head(self, data):
self.insert_at_nth(0, data)
def insert_at_tail(self, data):
self.insert_at_nth(len(self), data)
def insert_at_nth(self, index: int, data):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(-1, 666)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(1, 666)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(0, 2)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(0, 1)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(2, 4)
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(2, 3)
>>> str(linked_list)
'1->2->3->4'
>>> linked_list.insert_at_nth(5, 5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
"""
length = len(self)
if not 0 <= index <= length:
raise IndexError("list index out of range")
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.tail = new_node
elif index == 0:
self.head.previous = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
elif index == length:
self.tail.next = new_node
new_node.previous = self.tail
self.tail = new_node
else:
temp = self.head
for _ in range(index):
temp = temp.next
temp.previous.next = new_node
new_node.previous = temp.previous
new_node.next = temp
temp.previous = new_node
def delete_head(self):
return self.delete_at_nth(0)
def delete_tail(self):
return self.delete_at_nth(len(self) - 1)
def delete_at_nth(self, index: int):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> for i in range(0, 5):
... linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(0) == 1
True
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(3) == 5
True
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(1) == 3
True
>>> str(linked_list)
'2->4'
>>> linked_list.delete_at_nth(2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
IndexError: list index out of range
"""
length = len(self)
if not 0 <= index <= length - 1:
raise IndexError("list index out of range")
delete_node = self.head # default first node
if length == 1:
self.head = self.tail = None
elif index == 0:
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.previous = None
elif index == length - 1:
delete_node = self.tail
self.tail = self.tail.previous
self.tail.next = None
else:
temp = self.head
for _ in range(index):
temp = temp.next
delete_node = temp
temp.next.previous = temp.previous
temp.previous.next = temp.next
return delete_node.data
def delete(self, data) -> str:
current = self.head
while current.data != data: # Find the position to delete
if current.next:
current = current.next
else: # We have reached the end an no value matches
raise ValueError("No data matching given value")
if current == self.head:
self.delete_head()
elif current == self.tail:
self.delete_tail()
else: # Before: 1 <--> 2(current) <--> 3
current.previous.next = current.next # 1 --> 3
current.next.previous = current.previous # 1 <--> 3
return data
def is_empty(self):
"""
>>> linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
>>> linked_list.is_empty()
True
>>> linked_list.insert_at_tail(1)
>>> linked_list.is_empty()
False
"""
return len(self) == 0
def test_doubly_linked_list() -> None:
"""
>>> test_doubly_linked_list()
"""
linked_list = DoublyLinkedList()
assert linked_list.is_empty() is True
assert str(linked_list) == ""
try:
linked_list.delete_head()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen.
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen.
try:
linked_list.delete_tail()
raise AssertionError # This should not happen.
except IndexError:
assert True # This should happen.
for i in range(10):
assert len(linked_list) == i
linked_list.insert_at_nth(i, i + 1)
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 11))
linked_list.insert_at_head(0)
linked_list.insert_at_tail(11)
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(12))
assert linked_list.delete_head() == 0
assert linked_list.delete_at_nth(9) == 10
assert linked_list.delete_tail() == 11
assert len(linked_list) == 9
assert str(linked_list) == "->".join(str(i) for i in range(1, 10))
if __name__ == "__main__":
from doctest import testmod
testmod()
About this Algorithm
Singly Linked List is a linear and connected data structure made of Nodes. Each node is composed of a variable data where its content is stored and a pointer to the next Node on the list. The Linked List has a pointer to the first element of this Node sequence and may also have another pointer to the last Node to make operations at the far end less time-consuming. You can also store a length variable to store the total length.
A Doubly Linked List (DLL) contains an extra pointer, typically called previous pointer, together with next pointer and data which are there in singly linked list.
Advantages over singly linked list
- A DLL can be traversed in both forward and backward direction.
- The delete operation in DLL is more efficient if pointer to the node to be deleted is given.
- We can quickly insert a new node before a given node.
In singly linked list, to delete a node, pointer to the previous node is needed. To get this previous node, sometimes the list is traversed. In DLL, we can get the previous node using previous pointer.
Disadvantages over singly linked list
- Every node of DLL Require extra space for an previous pointer. It is possible to implement DLL with single pointer though (See this and this).
- All operations require an extra pointer previous to be maintained. For example, in insertion, we need to modify previous pointers together with next pointers. For example in following functions for insertions at different positions, we need 1 or 2 extra steps to set previous pointer.
Time Complexity
| Operation | Average | Worst |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Θ(n) | O(n) |
| Search | Θ(n) | O(n) |
| Insertion | Θ(1) | O(1) |
| Deletion | Θ(1) | O(1) |
Example
class LinkedList {
Node head; // Pointer to the first element
Node tail; // Optional. Points to the last element
int length; // Optional
class Node {
int data; // Node data. Can be int, string, float, templates, etc
Node next; // Pointer to the next node on the list
Node prev;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data) {
/* 1. allocate node
* 2. put in the data */
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL */
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
/* 4. change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
/* 5. move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_Node;
}
/* Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node after the given node */
public void InsertAfter(Node prev_Node, int new_data) {
/*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */
if (prev_Node == null) {
System.out.println("The given previous node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
/* 2. allocate node
* 3. put in the data */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
/* 5. Make the next of prev_node as new_node */
prev_Node.next = new_node;
/* 6. Make prev_node as previous of new_node */
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
/* 7. Change previous of new_node's next node */
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
}
Adding node at front
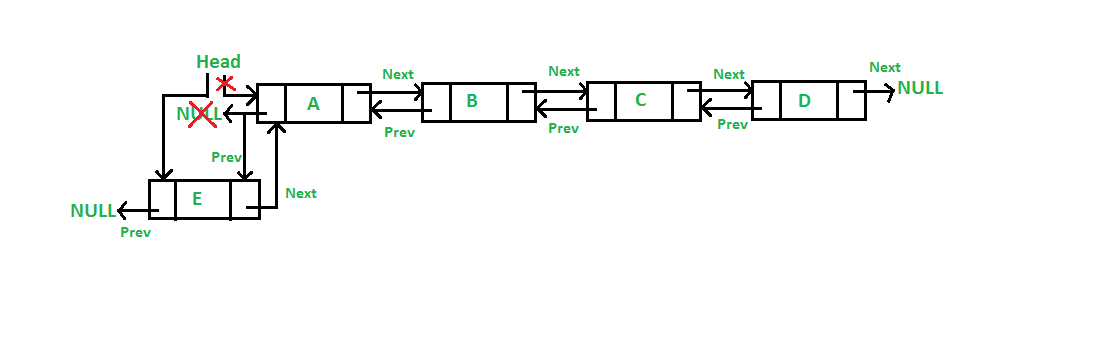
Add a node after a given node

Code Implementation Links
Video Explanation
A CS50 video explaining the Doubly Linked List Data Structure